S.R. Ranganathan introduced the concept of “five fundamental categories”, These Categories of PMEST stand for Personality, Matter, Energy, Space, and Time” identifying five essential categories that represent the core elements of any subject. According to Ranganathan, every subject or entity can be understood as a manifestation of one or more of these categories.
Here’s a brief explanation of each category:
- Personality: This refers to the unique characteristics or essence of a subject. It defines what makes the subject distinctive.
- Matter: This denotes the physical material or substance that constitutes the subject. It is the tangible aspect of the subject.
- Energy: This represents any action or process related to the subject. It encompasses the dynamic or functional aspects of the subject.
- Space: This category involves the geographical or spatial location associated with the subject. It refers to where the subject exists or operates.
- Time: This pertains to the temporal aspect or the time period related to the subject. It includes the duration or historical context of the subject.
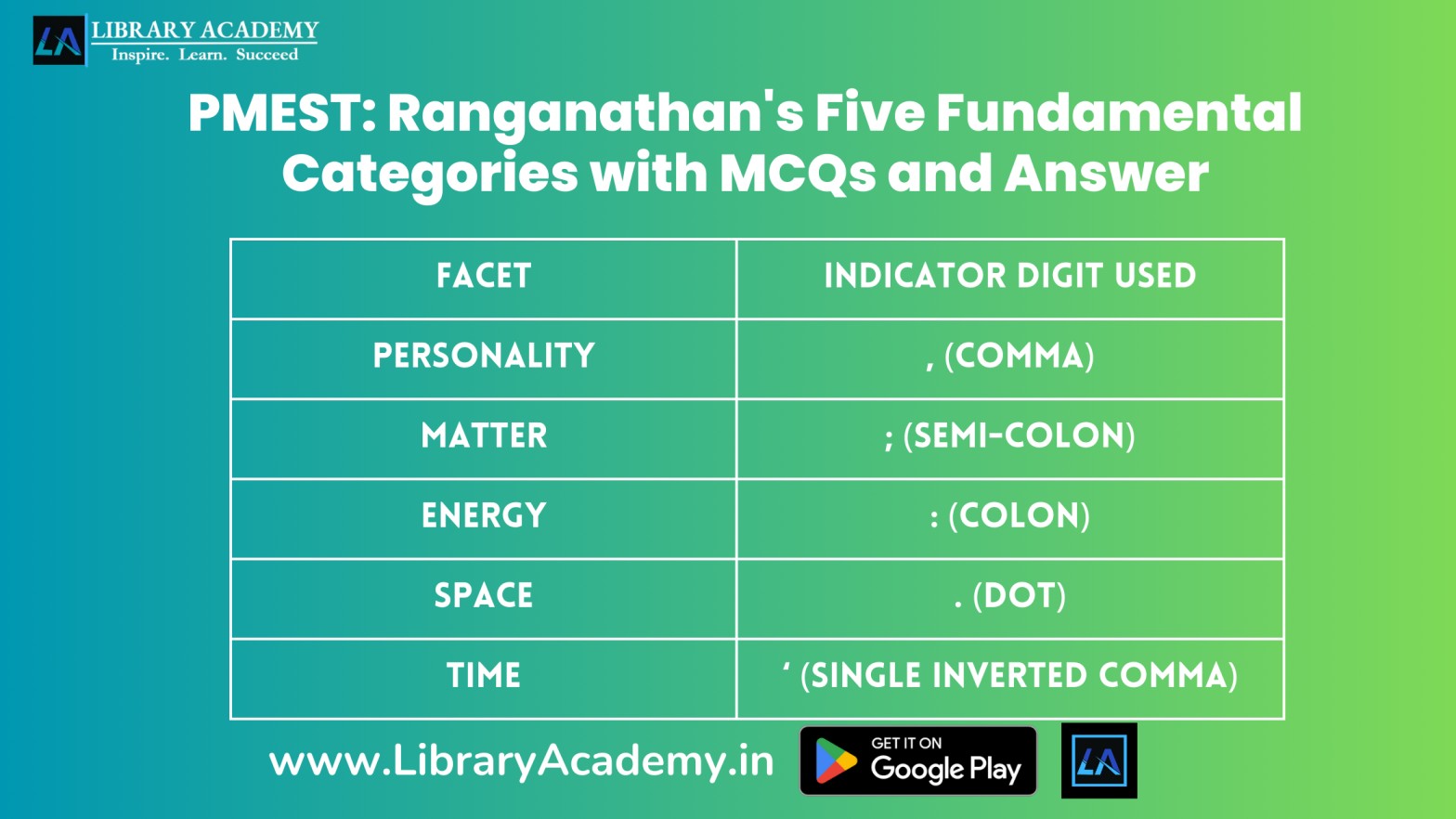
Here is the table with the facets and their corresponding indicator digits
| Facet | Indicator Digit Used |
|---|---|
| Personality | , (Comma) |
| Matter | ; (Semi-colon) |
| Energy | : (Colon) |
| Space | . (Dot) |
| Time | ‘ (Single inverted comma) |
MCQs with Answer on Ranganathan’s Five Fundamental Categories PMEST for UGC NET Library and Information Science, KVS Librarian, NVS Librarian, Bihar Librarian, etc
- What does PMEST stand for in Ranganathan’s fundamental categories?
- A) Physical, Matter, Energy, Space, Time
- B) Personality, Matter, Energy, Space, Time
- C) Process, Matter, Environment, Space, Time
- D) Physical, Matter, Energy, Space, Technology
- Answer: B) Personality, Matter, Energy, Space, Time
- Which category in PMEST represents the unique characteristics or essence of a subject?
- A) Matter
- B) Energy
- C) Personality
- D) Space
- Answer: C) Personality
- Which indicator digit is used for the category ‘Matter’?
- A) ,
- B) ;
- C) :
- D) .
- Answer: B) ;
- Which of the following categories involves the physical material or substance of a subject?
- A) Personality
- B) Energy
- C) Matter
- D) Time
- Answer: C) Matter
- What does the category ‘Energy’ refer to in Ranganathan’s framework?
- A) The physical material of the subject
- B) The spatial location of the subject
- C) Any action or process related to the subject
- D) The historical context of the subject
- Answer: C) Any action or process related to the subject
- Which indicator digit is associated with the ‘Energy’ category?
- A) ,
- B) ;
- C) :
- D) ‘
- Answer: C) :
- In Ranganathan’s fundamental categories, what does the ‘Space’ category refer to?
- A) The temporal aspect of the subject
- B) The unique characteristics of the subject
- C) The geographical or spatial location of the subject
- D) The physical material of the subject
- Answer: C) The geographical or spatial location of the subject
- Which of the following is NOT a fundamental category according to Ranganathan?
- A) Personality
- B) Matter
- C) Energy
- D) Process
- Answer: D) Process
- What indicator digit is used to represent the ‘Time’ category?
- A) ,
- B) ;
- C) :
- D) ‘
- Answer: D) ‘
- How does Ranganathan’s framework categorize the temporal aspect of a subject?
- A) Personality
- B) Matter
- C) Energy
- D) Time
- Answer: D) Time
- Which category is used to represent the physical material of a subject?
- A) Personality
- B) Matter
- C) Energy
- D) Space
- Answer: B) Matter
- What does the ‘Personality’ category define in Ranganathan’s system?
- A) The physical material of a subject
- B) The unique characteristics of a subject
- C) The actions related to the subject
- D) The geographical location of the subject
- Answer: B) The unique characteristics of a subject
- Which indicator digit is used for the ‘Space’ category?
- A) ,
- B) ;
- C) :
- D) .
- Answer: D) .
- In Ranganathan’s fundamental categories, what does ‘Energy’ encompass?
- A) The physical substance of the subject
- B) The spatial location of the subject
- C) The dynamic or functional aspects of the subject
- D) The historical context of the subject
- Answer: C) The dynamic or functional aspects of the subject
- Which indicator digit is used to represent the ‘Personality’ category?
- A) ,
- B) ;
- C) :
- D) ‘
- Answer: A) ,
- What aspect does the ‘Matter’ category focus on?
- A) The dynamic aspects of the subject
- B) The unique characteristics of the subject
- C) The physical substance of the subject
- D) The spatial location of the subject
- Answer: C) The physical substance of the subject
- Which category would cover the historical context or duration related to a subject?
- A) Personality
- B) Matter
- C) Energy
- D) Time
- Answer: D) Time
- What does the ‘Space’ category help to determine in Ranganathan’s framework?
- A) The unique characteristics of a subject
- B) The physical material of a subject
- C) The geographical location of a subject
- D) The actions related to the subject
- Answer: C) The geographical location of a subject
- In Ranganathan’s system, what does the indicator digit ‘;’ represent?
- A) Personality
- B) Matter
- C) Energy
- D) Space
- Answer: B) Matter
- According to Ranganathan, every subject or entity can be understood through the lens of how many fundamental categories?
- A) Three
- B) Four
- C) Five
- D) Six
- Answer: C) Five
Ranganathan’s fundamental categories provide a framework for understanding and classifying subjects by focusing on these five dimensions, which help in representing the main class of a subject comprehensively.
 Subscribe YouTube Channel
Subscribe YouTube Channel